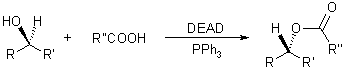
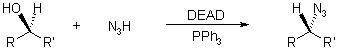
The Mitsunobu Reaction allows the conversion of primary and secondary alcohols to esters, phenyl ethers, thioethers and various other compounds. The nucleophile employed should be acidic, since one of the reagents (DEAD, diethylazodicarboxylate) must be protonated during the course of the reaction to prevent from side reactions.
Suitable nitrogen nucleophiles include phthalimide or hydrogen azide; subsequent hydrolysis (in the case of using phthalimide, see Gabriel Synthesis) or selective reduction (in the case of azide formation, see Staudinger Reaction) makes the corresponding amines accessible.
The triphenylphosphine combines with DEAD to generate a phosphonium intermediate that binds to the alcohol oxygen, activating it as a leaving group. Substitution by the carboxylate, mercaptyl, or other nucleophile completes the process.
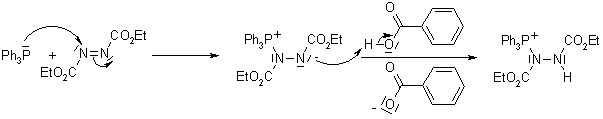
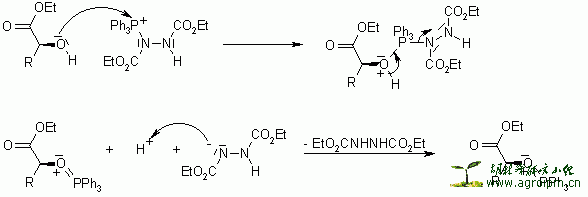
The reaction proceeds with clean inversion, which makes the Mitsunobu Reaction with secondary alcohols a powerful method for the inversion of stereogenic centers in natural product synthesis.

Side Reaction:
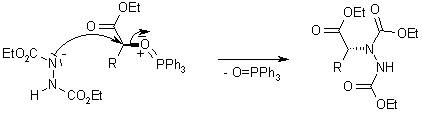
New protocols have been developed which allow better removal of side products and/or the conversion of more basic nucleophiles.
Recent Literature
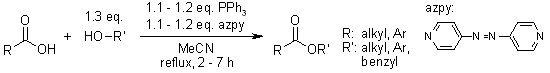
Easily Prepared Azopyridines As Potent and Recyclable Reagents for Facile Esterification Reactions. An Efficient Modified Mitsunobu Reaction
N. Iranpoor, H. Firouzabadi, D. Khalili, S. Motevalli, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 4882-4887.
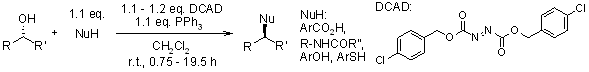
Simplification of the Mitsunobu Reaction. Di-p-chlorobenzyl Azodicarboxylate: A New Azodicarboxylate
B. H. Lipshutz, D. W. Chung, B. Rich, R. Corral, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 5069-5072.
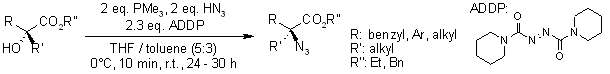
Mitsunobu Approach to the Synthesis of Optically Active α,α-Disubstituted Amino Acids
J. E. Green, D. M. Bender, S. Jackson, M. J. O'Donnell, J. R. McCarthy, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 807-810.
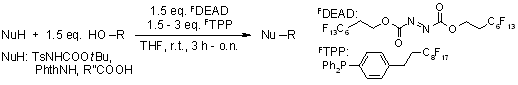
Fluorous Mitsunobu reagents and reactions
S. Dandapani, D. P. Curran, Tetrahedron, 2002, 58, 3855-3864.
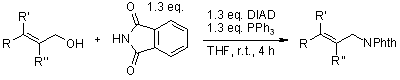
A convenient Two-Step Procedure for the Synthesis of Substituted Allylic Amines from Allylic Alcohols
S. E. Sen, S. L. Roach, Synthesis, 1995, 756-758.
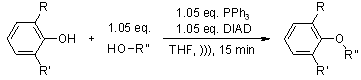
Use of Sonication for the Coupling of Sterically Hindered Substrates in the Phenolic Mitsunobu Reaction
S. D. Lepore, Y. He, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 8261-8263.

Organocatalytic Mitsunobu Reactions
T. Y. S. But, P. H. Toy, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 9636-9637.
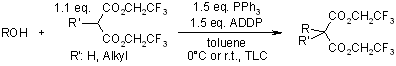
Carbon Nucleophiles in the Mitsunobu Reaction. Mono and Dialkylation of Bis(2,2,2-trifluorethyl) Malonates
J. M. Takacs, Z. Xu, X.-T. Jiang, A. P. Leonov, G. C. Theriot, Org. Lett., 2002, 4, 3843-3845.
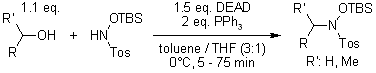
O-TBS-N-tosylhydroxylamine: A Reagent for Facile Conversion of Alcohols to Oximes
K. Kitahara, T. Toma, J. Shimokawa, T. Fukuyama, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 2259-2261.
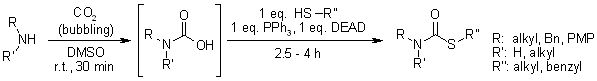
An Efficient, One-Pot Synthesis of S-Alkyl Thiocarbamates from the Corresponding Thiols Using the Mitsunobu Reagent
D. Chaturvedi, N. Mishra, V. Mishra, Synthesis, 2008, 355-357.
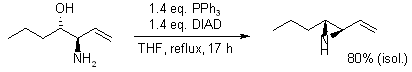
Synthesis of N-H vinylaziridines: a comparative study
B. Olofsson, R. Wijtmans, P. Somfai, Tetrahedron, 2002, 58, 5979-5982.
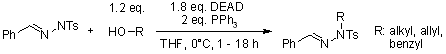
Exploration of the Mitsunobu Reaction with Tosyl- and Boc-Hydrazones as Nucleophilic Agents
J. M. Keith, L. Gomez, J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 7113-7116.
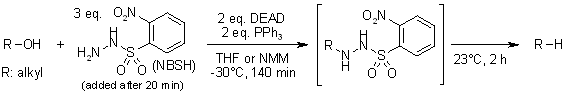
Single-Step Process for the Reductive Deoxygenation of Unhindered Alcohols
A. G. Myers, M. Movassaghi, B. Zheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 8572-8573.
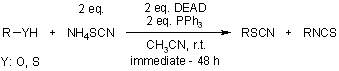
Conversion of Alcohols, Thiols, Carboxylic Acids, Trimethylsilyl Ethers, and Carboxylates to Thiocyanates with Triphenylphosphine/Diethylazodicarboxylate/NH4SCN
N. Iranpoor, H. Firouzabadi, B. Akhlaghinia, R. Azadi, Synthesis, 2004, 92-96.

以下内容转载自小木虫 哥特复兴VS [1]Han-Dong Sun,Yi-Ming Shi:LCUV-Guided Isolation and Structure Determination of Lancolide E: A Nortriterpenoid with a Tetracyclo [...

同一种微生物在不同的国家或地区常有不同的名称,这就是俗名。俗名在局部地区可以使用,但不便于交流,容易引起混乱。为在世界范围...

1 目的 规范TENSOR 27红外光谱仪的操作程序,正确使用仪器,保证设备安全和检测的顺利进行。 2 使用环境 电源电压:85~265V,47~65Hz 温度范...

人是能够思想的苇草 帕斯卡尔 人只不过是一根苇草,是自然界最脆弱的东西;但他是一根能思想的苇草。用不着整个宇宙都拿起武器来才能...