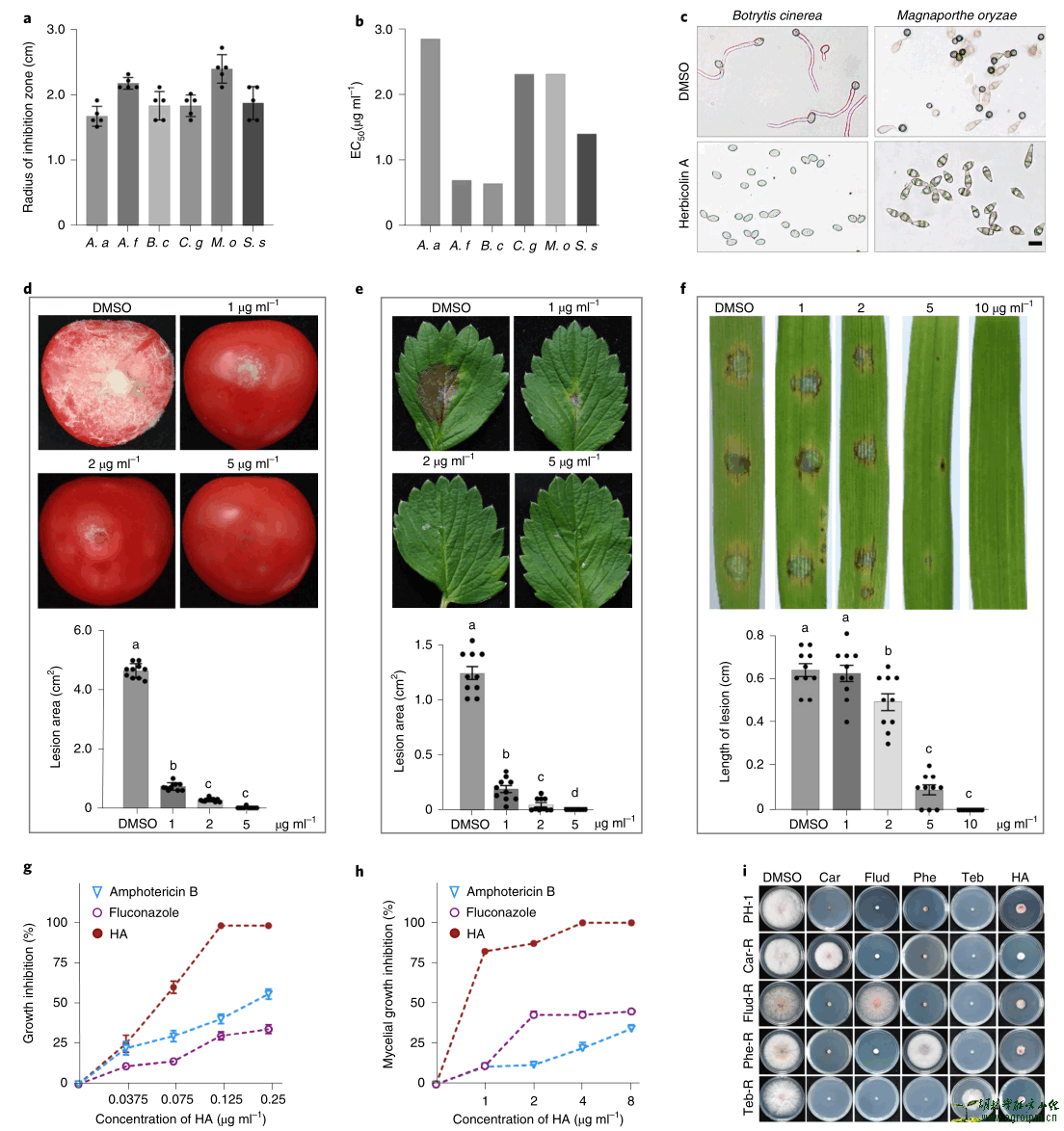
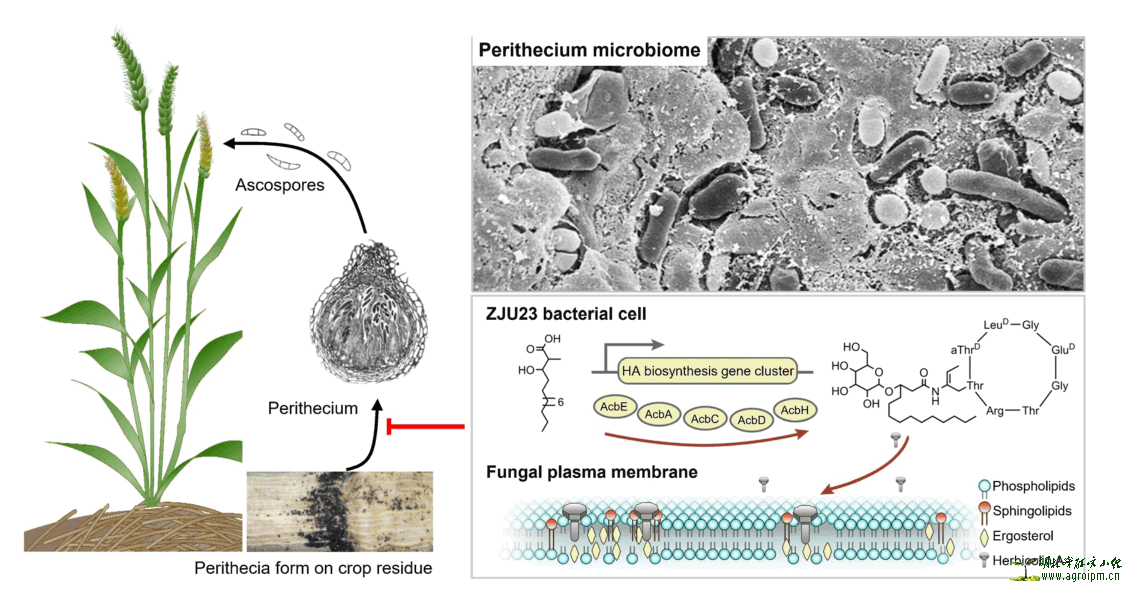
Abstract
Plant-pathogenic fungi form intimate interactions with their associated bacterial microbiota during their entire life cycle. However, little is known about the structure, functions and interaction mechanisms of bacterial communities associated with fungal fruiting bodies (perithecia). Here we examined the bacterial microbiome of perithecia formed by Fusarium graminearum, the major pathogenic fungus causing Fusarium head blight in cereals. A total of 111 shared bacterial taxa were identified in the microbiome of 65 perithecium samples collected from 13 geographic locations. Within a representative culture collection, 113 isolates exhibited antagonistic activity against F. graminearum, with Pantoea agglomerans ZJU23 being the most efficient in reducing fungal growth and infectivity. Herbicolin A was identified as the key antifungal compound secreted by ZJU23. Genetic and chemical approaches led to the discovery of its biosynthetic gene cluster. Herbicolin A showed potent in vitro and in planta efficacy towards various fungal pathogens and fungicide-resistant isolates, and exerted a fungus-specific mode of action by directly binding and disrupting ergosterol-containing lipid rafts. Furthermore, herbicolin A exhibited substantially higher activity (between 5- and 141-fold higher) against the human opportunistic fungal pathogens Aspergillus fumigatus and Candida albicans in comparison with the clinically used fungicides amphotericin B and fluconazole. Its mode of action, which is distinct from that of other antifungal drugs, and its efficacy make herbicolin A a promising antifungal drug to combat devastating fungal pathogens, both in agricultural and clinical settings.