
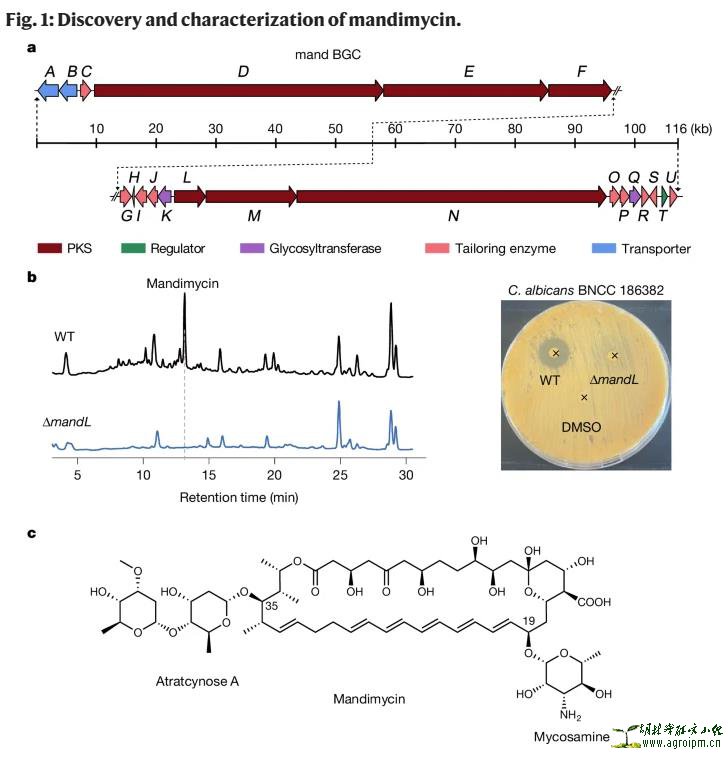
研究人员构建了放线菌生物合成基因簇数据库,并开发了基因挖掘模型,从31.6万株放线菌基因组中筛选出位于独立进化分支的多烯大环内酯类抗生素编码基因簇mand。通过微生物培养和代谢产物分离,成功发现了首个靶向真菌细胞膜磷脂的多烯大环内酯类抗生素Mandimycin。Mandimycin具有独特的化学结构,包括双糖基配体和5+1多烯片段,并在抗菌活性方面展现出三大核心优势:
1.广谱强效:在细胞实验和小鼠感染模型中,对包括多重耐药耳念珠菌在内的临床病原真菌均表现出强效杀菌活性,且在诱导耐药实验中未发现耐药菌株;
2.机制革新:通过双糖基配体靶向多种磷脂分子(如磷脂酰肌醇、磷脂酰乙醇胺、磷脂甘油等),进而破坏真菌细胞膜,突破了传统多烯类抗生素靶向细胞膜中的固醇分子(麦角甾醇和胆固醇)带来的靶点单一性;
3.安全性突破:动物试验表明,在相同杀菌条件下,Mandimycin的肾毒性和溶血性较两性霉素B显著降低,同时水溶性提升9700倍,为克服传统多烯大环内酯抗真菌药物的毒副作用提供了解决方案。
The global spread of multidrug-resistant pathogenic fungi presents a serious threat to human health, necessitating the discovery of antifungals with unique modes of action1. However, conventional activity-based screening for previously undescribed antibiotics has been hampered by the high-frequency rediscovery of known compounds and the lack of new antifungal targets2. Here we report the discovery of a polyene antifungal antibiotic, mandimycin, using a phylogeny-guided natural-product discovery platform. Mandimycin is biosynthesized by the mand gene cluster, has evolved in a distinct manner from known polyene macrolide antibiotics and is modified with three deoxy sugars. It has demonstrated potent and broad-spectrum fungicidal activity against a wide range of multidrug-resistant fungal pathogens in both in vitro and in vivo settings. In contrast to known polyene macrolide antibiotics that target ergosterol, mandimycin has a unique mode of action that involves targeting various phospholipids in fungal cell membranes, resulting in the release of essential ions from fungal cells. This unique ability to bind multiple targets gives it robust fungicidal activity as well as the capability to evade resistance. The identification of mandimycin using the phylogeny-guided natural-product discovery strategy represents an important advancement in uncovering antimicrobial compounds with distinct modes of action, which could be developed to combat multidrug-resistant fungal pathogens.

Xiangtao Meng a , b , Kevin J. Edgar a , b , , a Macromolecules and Interfaces Institute, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, United States b Department of Sustainable Biomaterials...
Ben Shen DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.031 The 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to William C. Campbell, Satoshi Omura, and Youyou Tu for t...

Self-Fueled Biomimetic Liquid Metal Mollusk Authors Jie Zhang, Youyou Yao, Lei Sheng, Jing Liu Abstract A liquid metal motor that can eat aluminum food and then move spontaneously a...

遗传, 2018, 40(10): 874-887 doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-169 综述 中国丝状真菌次级代谢分子调控研究进展 潘园园,1, 刘钢,1,2 1. 中国科学院微生物研究所,真...