Identification of a novel Streptomyces sp. strain HU2014
发布日期:2023-03-19 20:30 浏览次数:
Identification of a novel Streptomyces sp. strain HU2014 showing growth promotion and biocontrol effect against Rhizoctonia spp. in wheat
Hongxia Zhu, Linfeng Hu, Hai-Yan Hu, Feng Zhou, Shiwen Wang, Liuliu Wu, Tetiana Rozhkova, and Chengwei Li
Published Online: 3 Oct 2022 https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-06-22-1493-RE
Abstract
Wheat sharp eyespot is a serious disease caused by the phytopathogens Rhizoctonia cerealis and R. solani. Some species in the genus Streptomyces have been identified as potential biocontrol agents against phytopathogens. In this investigation, the physiological, biochemical, phylogenetic and genomic characteristics of the strain HU2014 indicate that it is a novel Streptomyces species most closely related to Streptomyces albireticuli. HU2014 exhibited strong antifungal activity against R. cerealis G11 and R. solani YL-3. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) on the four extracts from the extracellular filtrate of HU2014 identified 10 chemical constituents in the Natural Products Atlas with high match levels (more than 90%). In an antifungal efficiency test on wheat sharp eyespot, two extracts significantly reduced the lesion areas on bean leaves infected by R. solani YL-3. The drenching of wheat in pots with spore suspension of HU2014 demonstrated a control efficiency of 65.1% against R. cerealis G11 (compared with 66.9% when treated by a 30% hymexazol aqueous solution). Additionally, in vitro and pot experiments demonstrated that HU2014 can produce indoleacetic acid, siderophores, extracellular enzymes, and solubilized phosphate, and it can promote plant growth. We conclude that HU2014 could be a valuable microbial resource for growth promotion of wheat and biological control of wheat sharp eyespot.
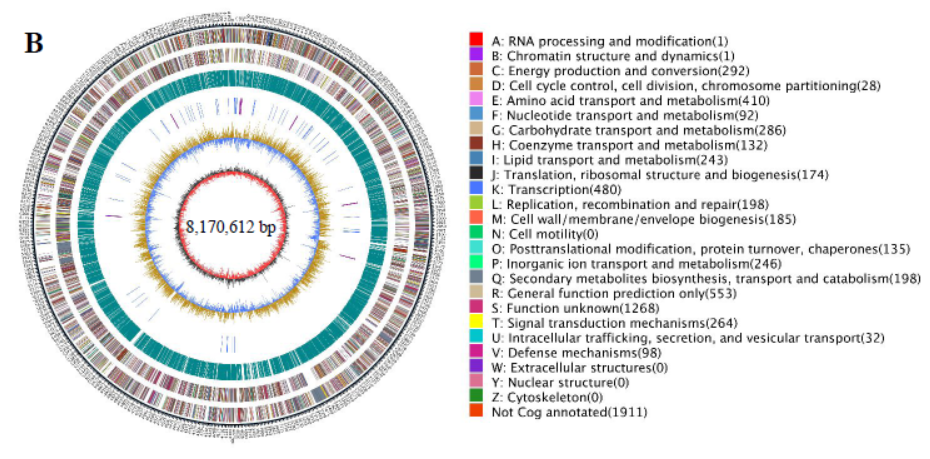
Identification assays of HU2014.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of HU2014 by Neighbor-Joining method based on 16S gene sequence and closely related species within the genus of
Streptomyces. Bootstrap values were indicated with the numbers at nodes and were obtained with 1,000 replications. The length of the branches reflected sequence divergence (percentage of base changes).
(B) Circular genome map for HU2014 using CG View. The outermost circle indicates the genome size. The second and third circles indicate CDS on forward and reverse strands colored according to COG category. The fourth circle is the repetitive sequences. The fifth circle shows the tRNA (blue) and rRNA (purple). The sixth circle shows G+C content in light yellow (+) and purple (-). The innermost circle shows the G+C skew in deep grey (G content more than C content) and red (G content less than C content). The scale is shown in the innermost circle.
